What is HDPE Plastic? Is Recycle Symbol 2 right for you?

Table of Contents
What does HDPE Mean?
HDPE is short for the chemical name high-density polyethylene.
Common Abbreviations and Names.
HDPE is also abbreviated polyethylene high-density (PEHD). And is known alternately as “Polythene”. Other common polyethylene derivatives that we may stock include LDPE, low-density polyethylene, and MDPE medium-density polyethylene.
High Density Polyethylene Properties
HDPE can be used for many applications. It is strong and flexible while light weight, with a low density. HDPE resin can withstand high heat for short durations, up to 120 degrees Celsius/248 degrees Fahrenheit. In containers, the natural color of HDPE resin is a smokey, translucent color, HDPE can be colored.
HDPE Plastic Uses
HDPE is one of the most widely used plastic resins in the world. Several years ago 30 million tons of HDPE resin was produced. What is it used for? Well, of course they are used for bottles and jars, as well as bottle and jar caps and lids. HDPE resin is also used for porch furniture, Tyvek brand house-wraps, electrical boxes, water and gas pipes, plastic bags and backyard storage sheds, to name a few applications.
HDPE plastic bottles and jars reduce breakage, are shatterproof for safety and allow for easy shelf stacking.
At Porter Bottle Company, we carry a wide variety of HDPE Plastic Bottles and Jars.
Can You Recycle HDPE?
Absolutely HDPE can be recycled! It is among the easiest and most frequent plastic resins to be recycled. It can be simply washed and melted for uses in products, or purified and re-polymerized to make new food-grade PET bottles and jars.
We encourage you to recycle your HDPE containers and pass the word on to your customers too! Containers made of HDPE can be identified at the bottom of most containers with the number 2 between the continuous recycle symbols.
How is HDPE Recycled?
Initially, the HDPE plastic containers are cleaned and then sorted as other plastic resins mixed in can spoil the recycling batch.
The HDPE bottles or jars are then shredded, melted and cooled. They are then turned into pellets which are re-used in the manufacturing process.
Scientific testing has shown that HDPE can be recycled and reused for new bottles at least ten times and may be used for other uses beyond that limit.
Are HDPE Plastic Containers Safe?
HDPE is not dangerous once it’s been made into the container that it will continue to be used for until it is recycled. HDPE is commonly used for food products thanks to regulations set out by the United States Food and Drug Administration. It should be mentioned that while all food-safe containers are made from HDPE, not all HDPE is food-safe.
Most importantly, all HDPE containers sold by Porter Bottle Company are food safe.
There has been a great deal of confusion about the safety of HDPE containers, especially following concerns raised about the safety of a different kind of plastic, which in the past contained bisphenol A (BPA) a substance formerly used to manufacture reusable rigid containers and electronic devices. There is no connection between HDPE plastic and BPA.
Containers in the United States have banned from using BPA since 1988. BPA is not used in the production of Polyethylene Plastics.
HDPE Science
According to Omnexus:
HDPE is a cost-effective thermoplastic with linear structure and no or low degree of branching. It is manufactured at low temperature (70-300°C) and pressure (10-80 bar) & derived from either modifying natural gas (a methane, ethane, propane mix) or catalytic cracking of crude oil into gasoline.
- Modifying natural gas (a methane, ethane, propane mix) or
- The catalytic cracking of crude oil into gasoline
HDPE is produced majorly using two techniques: Slurry Polymerization or Gas Phase Polymerization.
Properties of High Density Polyethylene
- HDPE Melting point: 120-140°C
- Density of HDPE: 0.93 to 0.97 g/cm3
- High Density Polyethylene Chemical resistance:
- Excellent resistance to most solvents
- Very good resistance to alcohols, dilute acids and alkalis
- Moderate resistance to oils and greases
- Poor resistance to hydrocarbons (aliphatic, aromatic, halogenated)
- Continuous temperature: -50°C to +60°C, relatively stiff material with useful temperature capabilities
- Higher tensile strength compared to other forms of polyethylene
- Low cost polymer with good processability
- Good low temperature resistance
- Excellent electrical insulating properties
- Very low water absorption
- FDA compliant
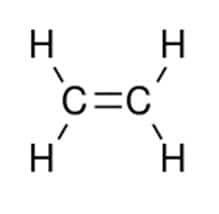
HDPE Is A Polymer Chain Composed Of Molecules Of Ethylene (C2H4)
Molecular Structure of Polyethylene is (C2H4)n